Computer Organization
TOC
CPU
- Control Unit
- A logic circuit that controls the CPU in respond of the given instructions.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit
- logic operations, shift operations, arithmetic operations
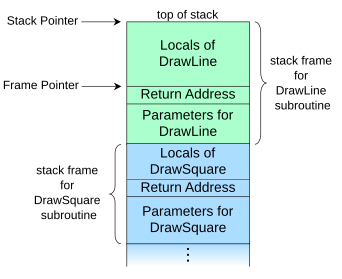
- Registers(basic C programming knowledge required)
- word size: 64 bits vs 32 bits
- User accessible:
- General purpose register: stores data or addresses
- Data register: stores data
- Address register: stores address
- Stack pointer: address of the top of the current program stack
- Base pointer: address of the starting position of the current stack frame
- Program counter: address of the next instruction
- Constant register: e.g. 0, pi
- Internal:
- Instruction register: current instruction being executed
- Memory address register: address of the data to be fetched/stored
- Memory data register: data to be fetched/stored
- I/O
Memory
- Addressing
- Smallest addressing unit in convention: byte
- Question:
- How many bits do you need in order to map 64 MB of memory?
- How much memory can you map with 32 bits?
- RAM: volatile
- ROM: contents written by manufacturer, can’t be erased
- PROM: contents can be write by user once, can’t be erased
- EPROM: a PROM that can be erased with UV light, requires physical removal
- EEPROM: a PROM that can be erased with electronic impulses
- Speed: RAM >> ROM
Cache
Acting as a memory device in between registers and main memory. - Size: x KB ~ x MB - Very efficient: frequently accessed data are usually in the minority. - Procedure: 1. CPU needs specific data 2. Check cache 1. Cache hit: Jump to 3 2. Cache miss: 1. Copy data from memory to cache 3. Get data from cache
Input/Output Devices
Nonstorage Devices
- Monitor
- Speaker
- Keyboard
- Touchpad
- Mouse
- Microphone
- Camera
- Printer
Storage Devices
Integrated Circuit
- SSD
Magnetic
- HDD
- Random Access
- Disks
- Tracks
- Sectors
- Performance:
- Slow, compared to SSD
- Rotational speed
- Seek time
- Seeking algorithms
- FCFS vs SSTF


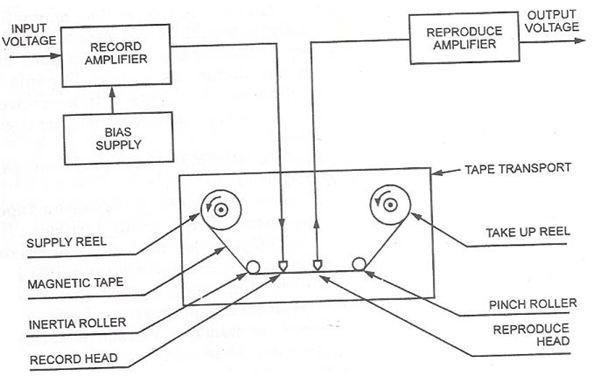
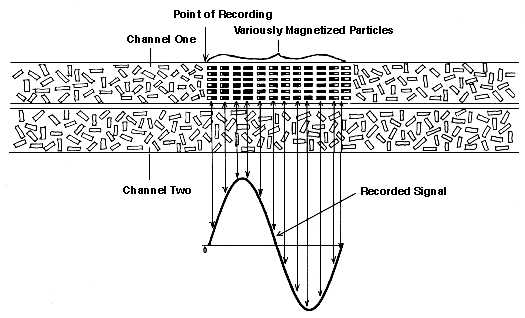
- Magnetic Tape
- Sequential Access
Optical
CD

- CD-ROM
- CD-R
- Simulated pits/lands
- Aluminum
- CD-RW
- Simulated pits/lands
- Gold
- Size: 650MB ~ 900MB
DVD
- Red laser
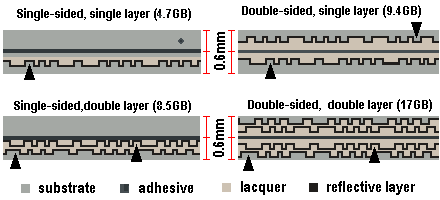
| Specification | Capacity |
|---|---|
| Single-sided, single-layer | 4.7 GB |
| Single-sided, dual-layer | 8.5 GB |
| Double-sided, single-layer | 9.4 GB |
| Double-sided, dual-layer | 17 GB |
Subsystem Interconnection
CPU and Memory Connection
- Data bus
- native support of 64 bit integer operations
- m bits data needs: m bits
- Address bus
- 32 bit limit: 4 GB
- 64 bit
- 2^m^ addresses needs: m bits
- Control bus
- 2^m^ control commands needs: m bits
I/O Connections
Port-mapped I/O (PMIO)
- == Isolated I/O
- Dedicated address space
- Dedicated instruction set
- Simple operations
Memory-mapped I/O (MMIO)
- Maps I/O to memory(combined address space)
Interrupt
- Emergency
Program Execution
Instructions
- Fetch
- Decode
- Execute
Input/Output
Programmed I/O
- CPU direct
- Issue command
- Constantly check availability
- Transfer
Interrupt I/O
- CPU direct
- Device interruption
- Transfer
Direct Memory Access
If there’s no DMA, CPU would be working on I/Os mostly!
- CPU indirect
- CPU issues command(what to do, starting address, number of bytes)
- DMA preperation
- DMA is ready and interrupts CPU
- CPU checks and gives bus permission to DMA
- DMA transfers data
- DMA finishes its job and intrrupts CPU
Instruction Set Architecture(ISA)
Complex Instruction Set Computer(CISC)
- Large set of complex and specialized instructions
- Complex instructions are translated into simple ones (microoperations)before executing.
- Architecture: x86, x86-64, Zen, Zen+, Zen2
- Products
- Intel: Core, Xeon…
- AMD: Ryzen…
- Target: Desktops, servers, etc.
Reduced Instruction Set Computer(RISC)
- Small set of simple and general instructions
- Usually: uniform instruction format, using single word with the opcode in the same bit positions for simpler decoding
- Architectures: ARM, MIPS, RISC-V
- Products: Cortex, Snapdragon
- Target: Smartphones, IOT devices…
Pipelining
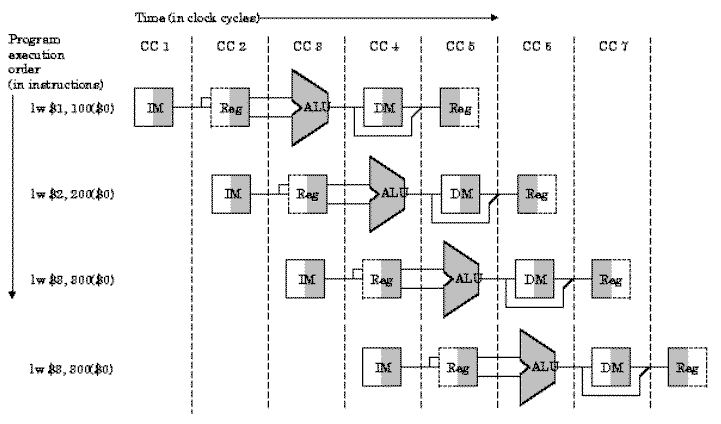
Parallel Processing
- SISD: non-parallel
- SIMD
- MISD?
- MIMD: Modern PCs
